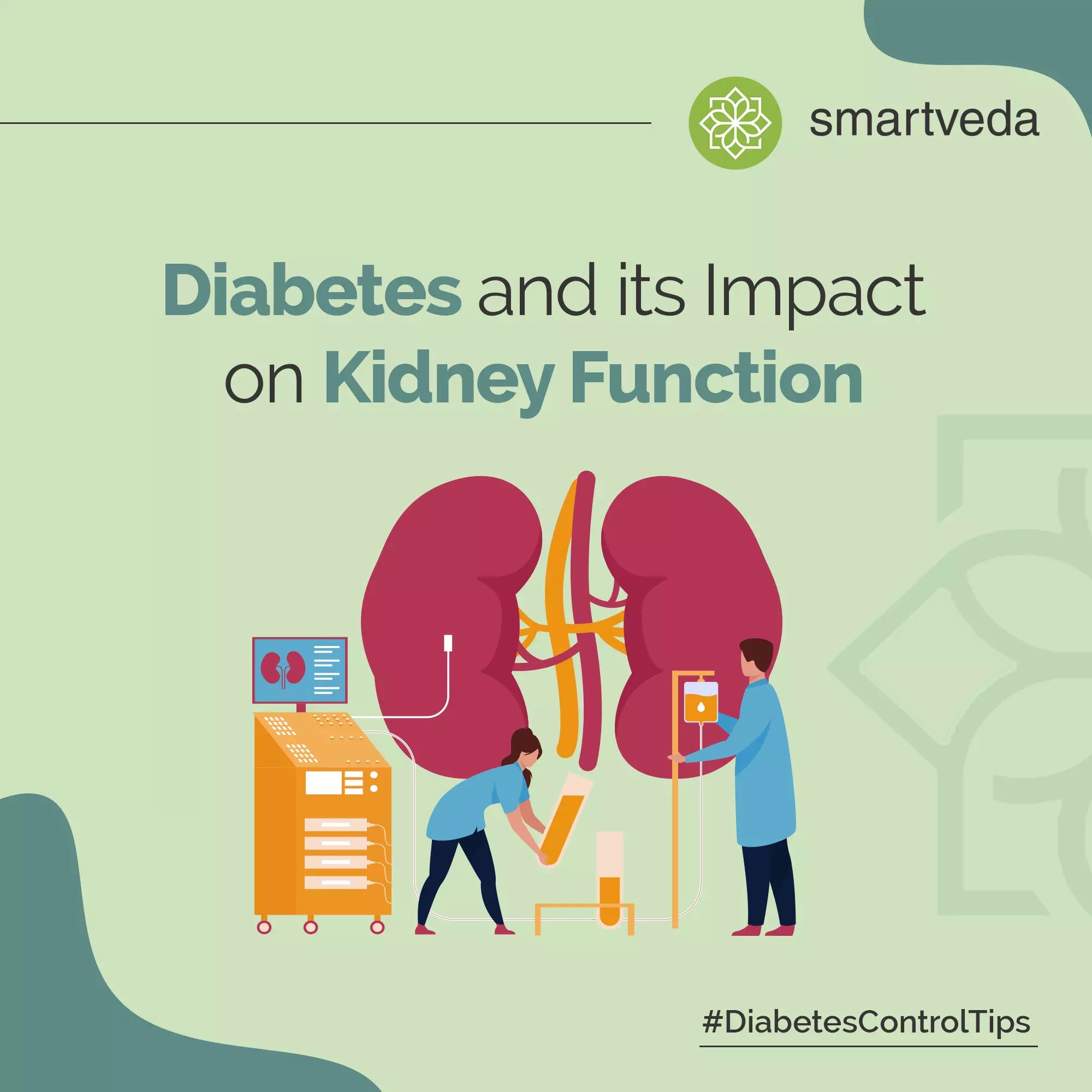
Water makes up more than half of the human body, thus staying hydrated is very important for everyone. Are you drinking enough water? According to Harvard University, water is essential for a range of daily bodily functions: 1. Transports nutrition and oxygen to your body's cells 2. Germs from your bladder is flushed 3. Helps you digest your food 4. Constipation is prevented. 5. Blood pressure is restored to normal. 6. Keeps your heart rate in check 7. Joints are cushioned 8. Protects your organs and tissues from a variety of potential damage 9. Regulates your body temperature 10. Keeps the electrolyte/sodium levels in your body in check Studies have shown that drinking water could help control blood sugar levels. When blood glucose levels are elevated, people with diabetes need more fluid. The kidneys can try to excrete excess sugar via urine as a result of this. Water does not increase blood glucose levels, which is why it is so important to drink when people with diabetes have high blood sugar because it allows more glucose to be filtered out of the system. Diabetes mellitus When the body attempts to expel excess glucose by urine, drinking water may help rehydrate the blood. Otherwise, the body would extract water from other sources, such as saliva and tears. If water is scarce, glucose cannot be excreted in the urine, further dehydrating the patient.
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes inspidus isn't linked to elevated blood sugar levels, but it does cause the body to produce a lot of urine. This can make people thirsty all of the time, putting them at risk of dehydration. Drinking more water may help alleviate these symptoms, and you may be advised to drink a specific amount of water a day by your doctor.
How much water should diabetics drink on a daily basis? There is no hard and fast rule regarding how much water you should drink, but we can follow some guidelines. The most crucial piece of advice is that you should always have water available and drink whenever you are thirsty. You don't have to force yourself to drink water to achieve a certain goal, but you should try to drink water throughout the day. Even if you aren't thirsty, try to drink a few sips of water every hour to stay hydrated. Because the thirst reflex isn't always perfect, especially in diabetics, so it’s better to
proactively drink a little water than risk dehydration. Drinking 8 glasses of water each day is recommended for non-diabetics, thus diabetics should certainly take this to heart. While our insulin-producing friends require adequate hydration as well, the effects of moderate dehydration on those of us with diabetes are more visible in our blood sugar levels.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. Increased urine and thirst are indicators of dehydration, and it's important to take early steps to rehydrate your body and keep your blood sugar in a healthy range. Dehydration can be life-threatening if left untreated, increasing the risk of kidney failure, seizures, and even coma. For similar content visit
Smartveda.co